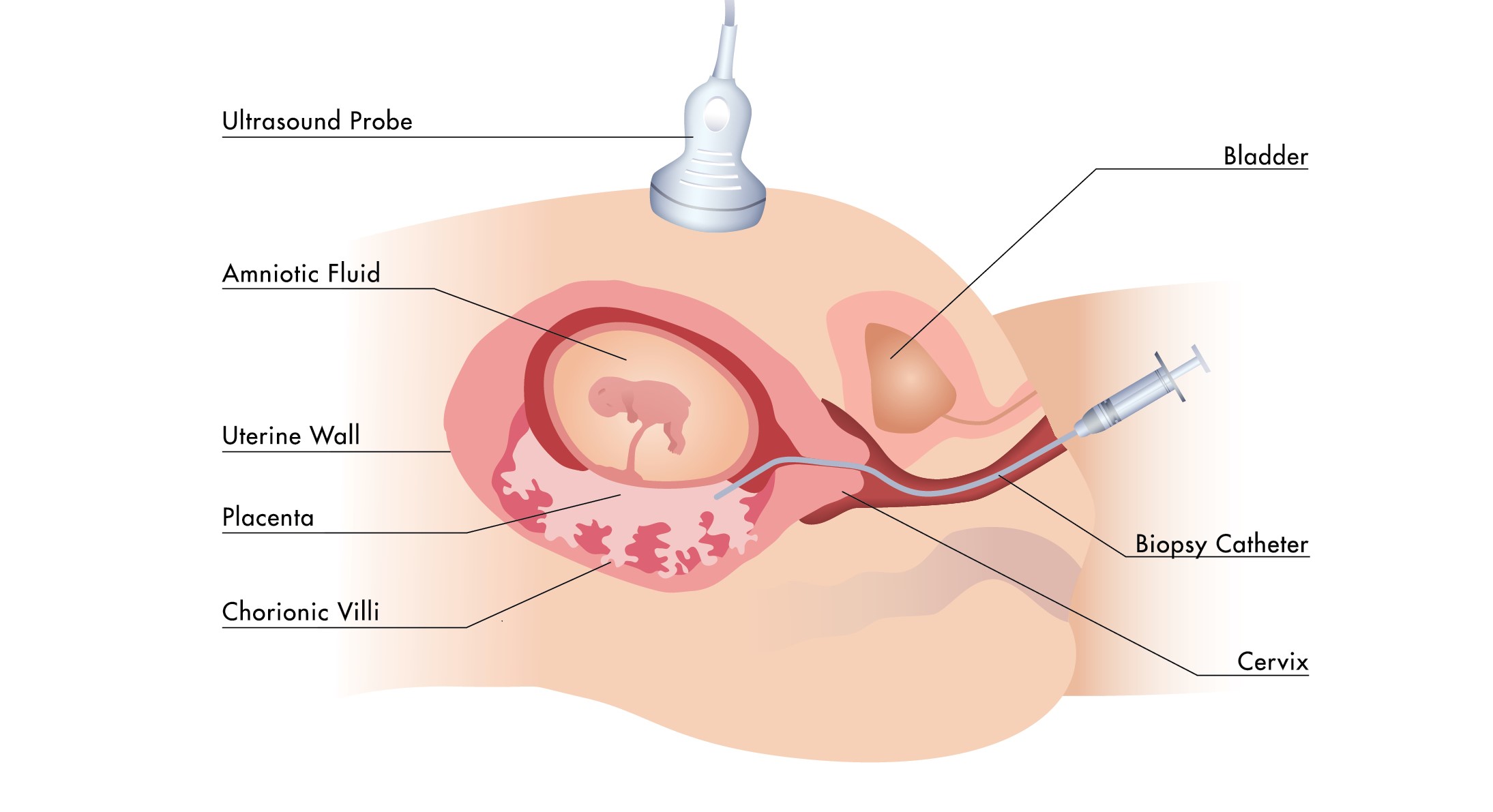
October 17, 2024
Prenatal testing has revolutionized obstetrics and gynecology, offering families crucial insights into the health of their unborn child. Two of the most important practices in this field are Chorionic Villus Sampling (CVS) and Amniocentesis. These tests provide families with peace of mind and aid in decision-making by identifying genetic and chromosomal disorders.
What is Amniocentesis?
Amniocentesis is a prenatal test performed between weeks 15 and 20 of pregnancy. During this procedure, a small amount of amniotic fluid, which surrounds the fetus in the uterus, is carefully extracted. This fluid contains fetal cells and various proteins that can be analysed to detect genetic conditions. By examining these cells and proteins, doctors can provide valuable information about the baby’s health and development.
Procedure of Amniocentesis:
Why is Amniocentesis Done?
Generally speaking, women who are more likely to give birth to a child who has a genetic problem should consider amniocentesis. Women over 35, those with a family history of genetic illnesses, and those whose prenatal test results have been abnormal are also included in this. It is capable of identifying ailments including spina bifida, cystic fibrosis, Down syndrome, and more.
Benefits and Risks:
Amniocentesis is a valuable diagnostic tool that provides highly reliable results for various conditions, but it does come with some risks. Because it's an invasive procedure, there’s a small chance of infection or miscarriage. It's important for parents to have a thorough discussion with their healthcare provider about these potential risks and benefits before deciding whether to proceed. This conversation can help ensure that they make an informed choice that aligns with their comfort levels and health goals.
What is Chorionic Villus Sampling (CVS)?
Another prenatal test that is carried out before amniocentesis is called Chorionic Villus Sampling, or CVS. It is usually carried out between the tenth and thirteenth weeks of pregnancy. Using CVS, a tiny sample of placental tissue which has the same genetic material as the fetus, allowing doctors to check for genetic conditions and other issues early on. This test offers vital information earlier in the pregnancy and can diagnose many of the same issues as amniocentesis.
Procedures of CVS:
Why is CVS Done?
CVS, like amniocentesis, is advised for women who are more likely to give birth to a child who has a genetic problem. It is capable of identifying diseases including sickle cell anemia, cystic fibrosis, Down syndrome, and other genetic abnormalities. Compared to amniocentesis, CVS has the benefit of early discovery, which enables quicker decision-making and, if necessary, intervention.
Benefits and Risks:
CVS offers the advantage of early implementation, which provides parents with more time to explore their options. However, like amniocentesis, CVS is an invasive procedure that carries risks, such as infection, miscarriage, and, if performed too early, potential limb abnormalities. Given these concerns, it’s essential for parents to have a detailed and supportive consultation with a healthcare professional. This ensures they are fully informed and can make the best decision for their situation.
Amniocentesis and Chorionic Villus Sampling (CVS) are important prenatal tests that help detect genetic conditions in a developing fetus. While both tests carry some risks, they offer valuable insights that can be crucial for early diagnosis and management of potential health issues. It's essential for parents to have open and detailed discussions with their healthcare providers to understand the benefits and risks, helping them make informed decisions that are best for their family's future.
At our clinic, we understand the importance of providing comprehensive and compassionate care for you and your baby. Whether you're considering amniocentesis or chorionic villus sampling (CVS), our specialised care team in fetal medicine is here to support you every step of the way. Our experienced professionals are dedicated to ensuring that you receive the best possible care, addressing any questions or concerns you might have with empathy and expertise. Your well-being and that of your baby are our top priorities, and we’re committed to guiding you through these important decisions with the utmost care and support.
October 9, 2024
The quality of life and general health of an individual can be greatly affected by blood diseases. Thalassemia and sickle cell disease are two examples of such hereditary blood disorders. Both disorders have an impact on the body's capacity to generate healthy red blood cells, which can result in many health issues.
What is Thalassemia?
Thalassemia is a genetic blood disorder that affects the body's ability to produce enough haemoglobin, the protein in red blood cells responsible for carrying oxygen throughout the body. When haemoglobin levels are low, it can lead to anaemia and other complications. There are two main types of thalassemia: alpha and beta thalassemia. Each type impacts a different part of the haemoglobin molecule, leading to varying symptoms and severity.
Alpha thalassemia occurs when there is a defect in one or more of the four alpha-globin genes. The severity depends on how many of these genes are affected. Beta thalassemia, on the other hand, involves defects in one or both of the two beta-globin genes. People with beta thalassemia may experience more severe symptoms, depending on whether one or both genes are affected.
Symptoms of Thalassemia:
The kind and degree of thalassemia can affect the symptoms. Typical signs and symptoms include:
Causes of Thalassemia:
If both parents carry the gene for thalassemia, there's a higher chance their child will inherit the condition. Thalassemia is passed down from parents who both have the trait, making it more likely for their child to develop the condition.
Handling and Medical Interventions:
Regular blood transfusions to keep haemoglobin levels in check, iron chelation therapy to eliminate extra iron from the body, and occasionally a bone marrow transplant are all part of the treatment for thalassemia. Effective management of Thalassemia necessitates an early diagnosis and continued medical attention.
Sickle Cell Disease: What Is It?
Sickle cell disease (SCD) is a genetic blood disorder where red blood cells become rigid and shaped like crescents or sickles instead of the usual round shape. These misshapen cells can block blood flow in small blood vessels, which can lead to pain, organ damage, and other serious health issues. The obstructed blood flow can cause severe pain episodes, known as crises, and may result in damage to organs like the spleen, liver, and kidneys.
Symptoms of Sickle Cell Disease:
People who have sickle cell disease may encounter:
Causes of Sickle Cell Disease:
Because sickle cell disease is inherited in an autosomal recessive manner, meaning a child must receive the sickle cell gene from both parents to have the disease. If both parents carry the gene, there's a 25% chance with each pregnancy that the child will have sickle cell disease. People of African, Mediterranean, Middle Eastern, and Indian origin are the most commonly affected by the illness.
Handling and Medical Interventions:
Managing sickle cell disease is all about improving quality of life and reducing complications. While there's no one-size-fits-all cure, a combination of treatments can help. Blood transfusions can ease symptoms by reducing the number of sickle cells. Pain management techniques, including medications and lifestyle adjustments, help manage the frequent pain crises. Hydroxyurea is a medication that can reduce the number and severity of these crises.
In certain cases, stem cell or bone marrow transplants might offer a potential cure, but this is generally considered only in specific situations due to its complexity and risks. Overall, care focuses on symptom management and preventing complications to help patients lead a more comfortable life.
Similarities between Thalassemia and Sickle Cell Disease:
Differences between Thalassemia and Sickle Cell Disease:
Sickle cell disease and thalassemia are serious blood disorders that require ongoing medical attention and care. For those living with these conditions, early diagnosis and regular monitoring can make a significant difference in managing symptoms and improving quality of life. Effective treatment and support are crucial for maintaining health and well-being. We can encourage research efforts and push for improved healthcare services for those in need by raising awareness and knowledge of these diseases.
When it comes to managing thalassemia and sickle cell disease, our clinic is committed to providing the highest level of care. We understand that these conditions can be complex and emotionally challenging, especially during pregnancy. That's why our specialized care team in fetal medicine is here to support you every step of the way. We combine expert medical knowledge with compassionate care to ensure the best possible outcomes for both you and your baby. You don’t have to face this journey alone—we’re here to guide you with expertise and empathy.
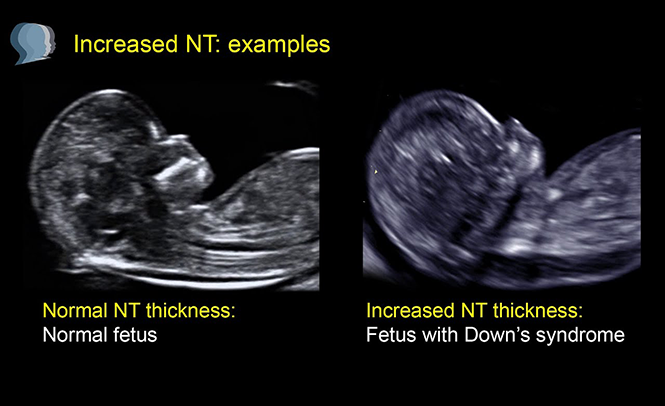
October 1, 2024
The Nuchal Translucency (NT) scan is a key ultrasound performed during early pregnancy, typically between 11 and 14 weeks. This test measures the fluid-filled space at the back of the baby's neck. The thickness of this area can give valuable insights into the baby’s health. A high NT scan result might be worrying for pregnant parents, so it’s crucial to understand what it means, the potential ramifications, and the next actions.
What is an NT Scan?
An NT (nuchal translucency) scan is a simple, non-invasive test done during the first trimester of pregnancy to check for the risk of certain chromosomal abnormalities in a developing baby. The scan measures the fluid or clear space at the back of the baby’s neck using ultrasound. Babies with certain conditions, like Down syndrome (trisomy 21), Edwards syndrome (trisomy 18), and Patau syndrome (trisomy 13), tend to have more fluid in this area, which can be detected during the scan.
The NT measurement is generally considered "raised" if it’s above 3.5 mm. The range can vary a bit depending on the baby's gestational age, but that’s the rough threshold.
For context:
But remember, even if the measurement is above this range, it doesn’t necessarily mean your baby has a problem. It simply means more testing or monitoring might be needed to rule out any issues.
What Does a Raised NT Scan Indicate?
A raised NT (nuchal translucency) measurement means that the fluid buildup at the back of the baby’s neck is thicker than usual. This can indicate:
Follow-Up Tests and Next Steps
To obtain a more comprehensive picture of your baby's health, your healthcare provider may probably suggest further testing if the results of your NT scan indicate an elevated measurement. These could consist of:
Emotional Support and Counseling:
It can be distressing and upsetting to learn that your NT scan is elevated. You must get assistance from your medical team, who can offer comprehensive information and help you with the following steps. Genetic counsellors can provide insightful advice and assist you in comprehending the consequences of the findings as well as your future alternatives.
Although an elevated NT scan result is not a conclusive diagnosis, it may indicate possible issues. It suggests that additional testing is necessary to fully assess your baby's health. You can obtain more insight into your unborn child's health and make knowledgeable decisions about your pregnancy by collaborating closely with your healthcare provider and making use of the available follow-up testing.
A raised NT scan can feel like a roadblock in what you hoped would be a smooth pregnancy journey. But it’s important to remember that this is just one chapter in your baby’s story. The NT scan is simply one tool among many that helps doctors monitor your pregnancy.
It’s natural to feel anxious, but remember that most babies with a raised NT scan are born healthy. Options like further screening tests or diagnostic procedures (e.g., CVS or amniocentesis) can provide clearer answers. These steps allow parents to be informed and prepared.
We understand that this is a deeply personal and emotional journey. At our clinic, we provide specialised fetal care with a compassionate, expert team ready to guide you through each step, ensuring you get the support and answers you need.
September 26, 2024
Infertility is a deeply personal and often emotional topic for many women and their families. It’s more common than most realize, affecting about 10-15% of couples worldwide. Yet, despite its prevalence, infertility can feel isolating, especially for those who are silently struggling with it. For women, the journey through infertility can be filled with frustration, heartache, and hope.
What Is Infertility?
Infertility is commonly defined as the inability to conceive after one year of unprotected intercourse. For women over the age of 35, this period is shortened to six months due to the natural decline in fertility with age. It's important to remember that infertility doesn't only affect women; it’s a shared challenge between both partners. In fact, approximately one-third of infertility cases are attributed to female factors, one-third to male factors, and the remaining cases are due to a combination of both or unexplained reasons.
Common Causes of Infertility in Women
Infertility in women can be caused by various factors, often related to issues with ovulation, fallopian tubes, the uterus, or hormonal imbalances. Understanding the root cause of infertility is key to finding the right treatment and support.
Diagnosing Infertility in Women
If a couple has been trying to conceive for a year without success, it’s recommended that they seek help from a healthcare provider. For women over 35, waiting six months is typically advised before consulting a specialist. The diagnostic process may include the following steps:
Treatment Options for Female Infertility
Thankfully, advances in medical science have created a variety of treatment options for women facing infertility. The choice of treatment depends on the underlying cause and the woman’s overall health. Here are some common treatments:
Facing infertility can be an emotionally challenging journey, but it’s important to remember that you are not alone. At our clinic, we’re committed to walking alongside you, offering compassionate care, advanced treatments, and personalised support. Whether you are just beginning your journey or have been searching for answers, our dedicated team is here to help you explore every option. Together, we can find the best path forward for your family’s future, offering both hope and expertise every step of the way.

September 18, 2024
Experiencing a miscarriage is one of the most heart-wrenching events that can happen to an expectant couple. When it happens more than once, the pain can feel overwhelming, as hope gives way to fear and doubt. Recurrent pregnancy loss (RPL) refers to having two or more consecutive pregnancy losses before 20 weeks of gestation, affecting about 1% of couples trying to conceive. While RPL can feel isolating, it’s important to know that it is not the end of the road. With modern medicine, awareness, and compassionate care, there are ways to navigate this challenging journey.
The Emotional Toll of RPL
When a pregnancy is lost, whether early or late, the grief is deeply personal. For many couples, it’s not just the loss of a baby but the loss of dreams, plans, and a future that was beginning to take shape. The emotional toll of recurrent pregnancy loss can be significant and multifaceted:
It’s crucial for couples to know that these feelings are normal and there is no “right” way to grieve. Seeking counselling or joining support groups can provide an outlet for these emotions and help in the healing process.
Understanding the Causes of RPL
For many, one of the most frustrating aspects of recurrent pregnancy loss is the lack of clear answers. In about 50% of cases, the cause of RPL remains unknown. However, research has identified several potential factors:
Diagnosis and Treatment: Navigating Next Steps
Once a couple experiences two or more consecutive losses, seeking medical advice from a fertility specialist or reproductive endocrinologist becomes important. Diagnosing the root cause of RPL can be a lengthy process, involving a range of tests including genetic screening, blood tests, and imaging studies like ultrasounds or hysteroscopies.
While it can be frustrating waiting for answers, many couples do eventually find a cause or a treatment plan that improves their chances of a successful pregnancy. Even when no specific cause is found, many couples still go on to have healthy babies with appropriate care.
Some potential treatments and interventions include:
Moving Forward with Hope
While recurrent pregnancy loss can feel like a never-ending cycle of hope and heartache, it’s important to remember that there is still hope. Many couples eventually go on to have successful pregnancies, whether naturally, through medical treatments, or with the help of assisted reproductive technologies like IVF.
It’s easy to get lost in the medical terms, tests, and statistics, but at the heart of it all are real people with real emotions, dreams, and desires. The journey through recurrent pregnancy loss is not easy, but it is one that can be navigated with support, care, and hope.
If you or someone you love is facing recurrent pregnancy loss, it can feel overwhelming and isolating. But you don’t have to go through this journey alone. At our clinic, our compassionate team of specialists is here to listen, understand, and work with you to find the best path forward. With the right care, support, and expertise, there is always hope for a brighter tomorrow.
September 11, 2024
Advances in technology have transformed prenatal care, providing expectant parents with critical insights into their baby's health. One of these breakthroughs is genetic ultrasonography, a specialized type of ultrasound that gives a detailed look at both the genetic health and development of the fetus. This tool allows doctors to detect potential genetic issues and track the baby’s growth more precisely, offering parents a clearer understanding of what to expect.
Genetic Ultrasound: What is It?
A genetic ultrasound, sometimes called a focused or detailed ultrasound, is a specialized type of prenatal imaging. Unlike routine ultrasounds, which provide a general view of the baby’s development, a genetic ultrasound offers a closer and more detailed examination. Its primary goal is to assess the baby’s physical features for signs that could indicate genetic conditions or congenital abnormalities.
Medical professionals use this advanced imaging technique to look for subtle markers that might not be visible in a standard ultrasound. These could include specific facial features, heart structures, or limb measurements that might suggest a genetic issue. Because it’s more focused, a genetic ultrasound can be an important tool in guiding further testing and giving families a clearer understanding of their baby’s health.
This extra level of detail is especially valuable in high-risk pregnancies or when there’s a concern based on family history or other screening results. With this information, doctors and parents can make more informed decisions about the pregnancy and prepare for any special care the baby might need after birth.
The Purpose of Genetic Ultrasound:
Early prenatal genetic problem screening and diagnosis is the main objective of genetic ultrasonography. The procedure is usually carried out between weeks 18 and 22, which is an important time when numerous fetal structures are established and can be examined for anomalies. The following are some typical justifications for suggesting a genetic ultrasound:
During a Genetic Ultrasound: What to Expect?
A genetic ultrasound is a non-invasive procedure that uses high-frequency sound waves to create detailed images of a developing fetus. This specialized ultrasound goes beyond standard imaging, offering insights into potential genetic conditions or abnormalities. Typically conducted in the second trimester, it helps assess specific physical markers that might indicate chromosomal issues like Down syndrome. Parents often find this method reassuring because it provides a thorough look at their baby’s development without the risks associated with invasive procedures like amniocentesis. What parents can anticipate from the procedure is as follows:
Benefits of Genetic Ultrasound:
Genetic ultrasonography is a useful technique in prenatal treatment because of its many advantages:
1. Early Detection: Parents and healthcare professionals can make educated decisions regarding the pregnancy and get ready for any necessary medical procedures when possible genetic abnormalities are identified early.
2. Peace of Mind: Knowing their child is developing healthily is a source of comfort and peace of mind for many parents, who receive a normal genetic ultrasound.
3. Personalized Care: Prenatal care and birth plans can be customized by medical professionals based on the results of genetic ultrasounds to suit the unique needs of the mother and child.
A significant achievement in prenatal care, genetic ultrasonography offers precise insight into the health and development of the fetus. It enables parents and healthcare professionals to take proactive measures in guaranteeing the best possible outcomes for mother and kid by discovering probable genetic anomalies early. With the knowledge and assurance that come with being a parent, embrace the adventure with the insights provided by genetic ultrasonography.
At LFMC, we understand that the journey through pregnancy is deeply personal and often filled with questions. That’s why we offer specialized genetic ultrasound services, delivered by a dedicated care team with expertise in fetal medicine. Our compassionate professionals are here to support you every step of the way, ensuring you receive the highest quality of care and attention. Your peace of mind is our priority, and we are committed to providing you with the information and support you need for a healthy pregnancy.
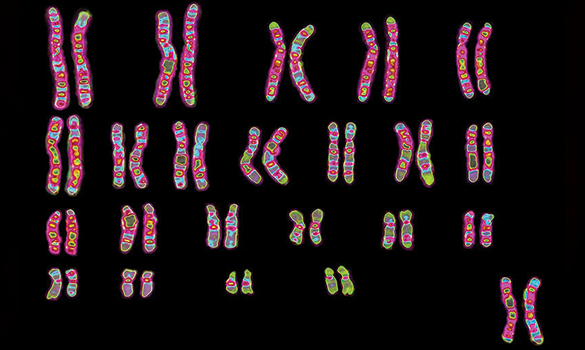
September 4, 2024
Every cell in our body has a unique genetic blueprint that shapes who we are. This blueprint is found in our DNA, which is organised into structures called chromosomes. Karyotyping is a helpful tool that lets us see and examine these chromosomes. By doing this, doctors can check if there are any issues with the number or structure of chromosomes, which can be important for diagnosing genetic conditions or understanding genetic health.
What is a Karyotype?
Imagine your body as a beautifully complex puzzle, with each piece playing a crucial role in creating who you are. This puzzle is your genetic blueprint, written in the language of DNA and organized into structures called chromosomes. But how do we make sure everything is in the right place and functioning correctly? That’s where karyotyping comes in.
Karyotyping is like taking a snapshot of your chromosomes, the tiny thread-like structures inside your cells that carry your genetic information. To get this snapshot, doctors use a special test that can be done in a few different ways.
How is a Karyotype Created?
What Makes Karyotyping Crucial?
Several essential purposes of karyotyping in medicine and research are as follows:
Types of Chromosomal Abnormalities Detected by Karyotyping
The Drawbacks of Stereotyping
Although karyotyping is an effective technique, it has drawbacks:
Progress Beyond Karyotyping
More complex genetic analysis techniques have been made possible by technological advancements:
Karyotyping is like taking a detailed look at a baby’s chromosomes to check for any abnormalities. By examining these chromosomes, doctors can spot issues that might affect the baby’s health.
In conclusion, understanding your baby’s chromosome patterns through karyotyping can provide valuable insights and help you make informed choices about your pregnancy. It’s all about giving you the information you need to prepare and support your family in the best way possible.

August 29, 2024
A journey full of excitement and transformation, pregnancy is also a time of many decisions. Prenatal screening is one of the most important factors, especially for aneuploidy. An aberrant amount of chromosomes in a cell is referred to as aneuploidy, and it can cause a variety of genetic problems. An essential part of prenatal care is screening for aneuploidy, which offers important insights into the growing baby's health.
Aneuploidy: What Is It?
The human body is composed of a vast number of cells, each of which contains essential genetic information stored in the form of chromosomes. When a cell has an unusually high number of chromosomes, it is called aneuploidy. Humans typically have 46 chromosomes, which are paired off into 23 pairs. An additional chromosome (trisomy) or a missing chromosome(monosomy) are the two outcomes of aneuploidy. Typical aneuploidies consist of:
Why Is Screening for Aneuploidy Important?
1. Prompt Identification and Evaluation
Screening for aneuploidy helps identify chromosomal problems early in pregnancy. This early detection allows parents and healthcare providers to make informed decisions about further tests, medical care, and next steps. It provides crucial information to help parents prepare emotionally, financially, and medically for the arrival of a child who may have special needs.
2. Tailored Antenatal Care
The results of prenatal screenings help tailor care to each pregnancy's specific needs. For instance, if a screening shows a higher risk of aneuploidy, doctors might recommend further tests like amniocentesis or chorionic villus sampling (CVS). This way, a personalised care plan can be made to monitor and manage any possible issues.
3. Informed Decision-Making
Aneuploidy screening gives parents crucial information about their baby's health. This knowledge helps them make important decisions, such as whether to continue the pregnancy, consider adoption, or prepare for a child with special needs. It also allows parents to seek out resources and support early on.
Types of Screening Tests for Aneuploidy
Translucency nuchal (NT) Ultrasound: It calculates the amount of fluid behind the baby's neck.
Blood tests: Determines levels of human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) and pregnancy-associated plasma protein-A (PAPP-A).
Fetal DNA that is floating about in the mother's blood is examined by NIPT. It can be performed as early as the tenth week of pregnancy and is incredibly accurate. In addition to screening for common trisomies, NIPT can identify the sex of the infant.
Quad Screen: Determines the mother's blood levels of four chemicals: alpha-fetoprotein (AFP), human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG), estriol, and inhibin-A. It provides important information that can guide further diagnostic testing and prenatal care.
While screening tests can indicate the likelihood of aneuploidy, diagnostic tests like amniocentesis and CVS provide a definitive diagnosis. These tests involve extracting and analysing cells from the amniotic fluid or placenta to check for chromosomal abnormalities.
Interpreting the Screening Results
Aneuploidy screening gives an idea of the risk rather than a definite answer. For example, the results might show a chance like 1 in 1,000 that the baby could have a chromosomal issue. If the screening suggests a higher risk, more detailed tests, like amniocentesis or chorionic villus sampling (CVS), might be recommended to get clearer answers about the baby's genetic health.
Aneuploidy screening is a vital part of prenatal care, offering parents valuable insights into their baby's health. By identifying potential genetic issues early on, it allows families to make informed decisions and prepare for the future, whether that means embracing the joys and challenges of raising a child with special needs or exploring other options. Understanding the importance of this screening empowers parents to provide the best possible start for their baby, surrounded by the right support and resources.
At our hospital, we prioritise your family’s peace of mind by offering comprehensive aneuploidy screening, backed by a specialised fetal medicine care team. Our team members are dedicated to providing you with personalised support throughout your pregnancy journey. From consultation to testing and beyond, you can trust that you and your baby are in the best hands possible. We’re here to guide you every step of the way with compassion, expertise, and a deep commitment to your well-being.
August 19, 2024
Pregnancy also involves a series of tests and ultrasounds that are essential for tracking the health and development of the unborn baby. One of the critical aspects of these ultrasounds is assessing the baby's nasal bone, especially in the first trimester. An absent nasal bone is a finding that can cause anxiety for expectant parents, and it’s important to understand what it really means, its implications, and the next steps. The nasal bone is an important anatomical feature during fetal development, and its existence or absence can provide important information about a developing baby's health and growth. When a prenatal screening finds a missing nasal bone, it may be a sign of specific chromosomal disorders.
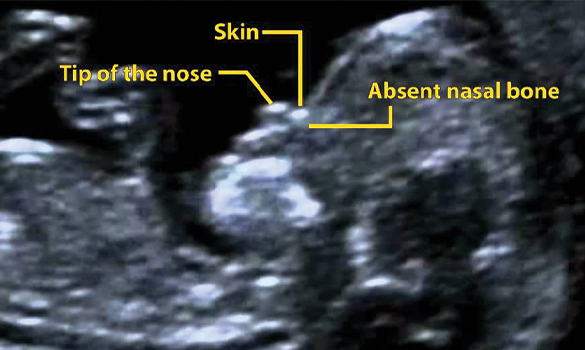
What is the Nasal Bone, and Why is it Important?
The nasal bone is a small bone in the face that supports the nose structure. In a developing fetus, it usually starts forming early in pregnancy and can typically be detected on an ultrasound between the 11th and 14th weeks of gestation. During a routine ultrasound at this stage, the sonographer measures several markers that help assess the baby’s growth and screen for potential chromosomal abnormalities. The nasal bone is one of these critical markers.
In certain pregnancies, the nasal bone may not be visible on the ultrasound, and this is commonly referred to as an “absent nasal bone.” This finding can be associated with an increased risk of chromosomal abnormalities, particularly Down syndrome (trisomy 21). Studies have shown that a significant percentage of babies with Down syndrome have an absent or hypoplastic (underdeveloped) nasal bone.
Reasons for a Missing Nasal Bone
Diagnosis
Early detection of potential concerns allows for more informed decision-making. Whether it’s choosing further testing or preparing for the possibility of a special-needs child, having the information early can empower you to plan ahead.
Consequences for the Baby
If a baby's nasal bone isn't visible during an ultrasound, it might suggest a higher chance of a chromosomal issue, but it doesn't mean there's definitely a problem. If further tests show something unusual, the parents and doctors will discuss what that could mean and what options are available. It's important to note that many babies born without a visible nasal bone can still be perfectly healthy, especially if there are no other signs of a problem.
Practical and Emotional Aspects for Parents to Consider
For pregnant parents, learning that a nasal bone is missing might be distressing. Having a healthcare team that is supportive and able to offer guidance and clear information is essential. Genetic counselling can help parents make educated decisions regarding their children by helping them understand the potential dangers and ramifications of their pregnancy.
Pregnancy is a time filled with so many emotions, hopes, and dreams. When faced with unexpected findings like an absent nasal bone, it’s important to approach the situation with as much information and support as possible. Every pregnancy is unique, and so is every baby. Regardless of the outcome, remember that you have options, support, and resources available to you. Stay informed, stay positive, and trust that you and your baby are on a journey that is uniquely yours.
The absence of a nasal bone in a prenatal ultrasound can be a significant indicator for certain genetic conditions, but it's essential to remember it's just one piece of the puzzle. This finding may warrant further testing and discussion with healthcare providers to fully understand its implications. While it can be concerning, having the right information and support helps parents navigate their options and prepare for their baby's future. By staying informed and proactive, families can ensure they are making the best choices for their child's health and well-being.
Our experts will guide you through every step, offering clear information, compassionate care, and the best options for your unique situation. With our state-of-the-art facilities and a team that truly understands the nuances of fetal medicine, we are here to support you and your family with confidence and care. You can trust that you’re in good hands with our dedicated specialists who are committed to ensuring the best possible outcomes for you and your baby.
August 13, 2024
Fetal medicine is a branch of medicine that focuses on the health and development of a fetus during pregnancy. This specialized field has evolved significantly over the years, offering expectant parents more information and options than ever before. In this blog, we’ll explore the essentials of fetal medicine, from what it involves to how it impacts families, all while keeping the discussion warm and relatable.
What is Fetal Medicine?
Fetal medicine, also known as maternal-fetal medicine, is a subspecialty of obstetrics. It involves diagnosing, managing, and treating conditions that affect a developing fetus. This field combines advanced technology with compassionate care to monitor the health of both mother and baby throughout pregnancy.
Why is Fetal Medicine Important?
Pregnancy is a complex journey, and fetal medicine plays a crucial role in ensuring that both the mother and the fetus are as healthy as possible. Here’s why it matters:
Key Aspects of Fetal Medicine
Fetal medicine encompasses a range of practices and procedures, each designed to provide insight into the health of the fetus and address any issues that may arise. Here are some of the key components:
1. Screenings and Tests
2. Monitoring and Management
The Human Side of Fetal Medicine
While the technology and procedures in fetal medicine are incredibly advanced, at its core, this field is about supporting families during one of the most important times of their lives. Here’s how fetal medicine professionals make a difference on a personal level:
1. Empathy and Support
Fetal medicine specialists understand that expecting parents are navigating a wide range of emotions, especially when faced with potential complications. They provide not just medical care but also emotional support, helping families understand their options and feel reassured throughout the process.
2. Clear Communication
Medical jargon can be overwhelming. Specialists in fetal medicine strive to communicate complex information in a way that is clear and understandable. They take the time to answer questions and ensure that parents are fully informed about their choices.
3. Family-Centered Care
Fetal medicine is not just about the fetus but also about the family as a whole. Specialists work closely with parents, and sometimes extended family, to ensure that everyone is on the same page and that the care plan aligns with the family’s values and preferences.
Advances in Fetal Medicine
The field of fetal medicine continues to evolve, with new technologies and approaches constantly being developed. Some exciting advancements include:
In the journey of pregnancy, the path to understanding and managing fetal health is both profoundly personal and crucial. At LFMC, we recognize that each pregnancy is unique, and the care you receive should reflect that. Our specialized team in fetal medicine is dedicated to providing advanced, compassionate care tailored to your needs. With a deep understanding of the latest medical technologies and a commitment to personalized support, we strive to ensure that you and your baby receive the best possible care every step of the way. Our goal is not just to provide medical expertise but to be a source of reassurance and support during this important time.